Authored by:
Adrian Iliescu (Aliant+ Accounting Member / Romania)
Agnieszka Wagemann–Smolańska (Aliant Law Firm / Poland)
Audrius Bitinas (Aliant Law Firm / Lithuania)
Elisa Noto (Aliant Law Firm / Italy)
Enrique Schinelli Casare (Aliant+ Law Member / Argentina)
Gideon Koren (Aliant Law Firm / Israel)
Magda Stárková (Aliant+ Law Member / Czech Republic)
Petar Kecman (Aliant+ Accounting Member / Serbia)
Rastislav Rosko (Aliant+ Law Member / Slovakia)
Ron Meulmeester (Aliant+ Law Member / The Netherlands)
Introduction
Receiving a job offer in another country can be an exciting opportunity, but what happens if you lose your job abroad? Understanding the unemployment insurance (UI) systems of different countries is essential for ensuring financial security and planning for unexpected job loss.
What is Unemployment Insurance (UI)?
Unemployment insurance is a vital component of social protection systems worldwide. It provides financial stability and helps preserve human capital during periods of unemployment. UI benefits are typically part of labor contracts and are designed to:
- Protect individuals from immediate poverty during unemployment.
- Encourage job-seeking and skill development to improve employability.
How Unemployment Insurance is Funded
Unlike social assistance, UI benefits are funded primarily through contributions from employees and employers. This horizontal redistribution of funds across an individual’s life phases allows for financial security in times of need. In most cases, these benefits can be accessed even outside the country where contributions were made, though time restrictions may apply in certain situations.
The Benefits and Trade-Offs of Unemployment Insurance
Unemployment insurance offers both advantages and challenges:
- Insurance Value: UI helps individuals maintain their standard of living by smoothing consumption during unemployment.
- Efficiency Costs: Extended benefits may lead to longer unemployment durations, delaying re-employment.
A well-designed UI system strikes a balance between these factors and often includes active labor market policies to support job seekers in re-entering the workforce.
The Role of UI During Economic Crises
UI serves as an economic stabilizer during crises. By decreasing sensitivity to economic shocks, it reduces fluctuations in aggregate income, employment, and consumption. This stabilization effect is particularly significant in high-income countries, where informal employment is less prevalent. In regions with high levels of informal employment, there is a risk of individuals claiming UI benefits while working informally.
Unemployment Insurance and International Human Rights
The right to social security, including unemployment protection, is enshrined in various international human rights documents:
- Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948): Article 22 recognizes the right to social security.
- International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (1966): Article 9 emphasizes unemployment protection.
- International Labour Organization (ILO) Convention 102: Article 20 highlights the need to protect individuals from income suspension due to unemployment.
Conclusion
Understanding the unemployment insurance system in a foreign country is critical for expatriates and international job seekers. These systems not only provide financial security but also support economic stability during challenging times. As global labor markets evolve, ensuring access to robust unemployment insurance schemes will remain a key component of sustainable social protection.
If you have questions about unemployment insurance policies or need assistance with matters related to unemployment insurance in your country, our team of experienced attorneys is here to help. Contact us for expert advice tailored to your situation.
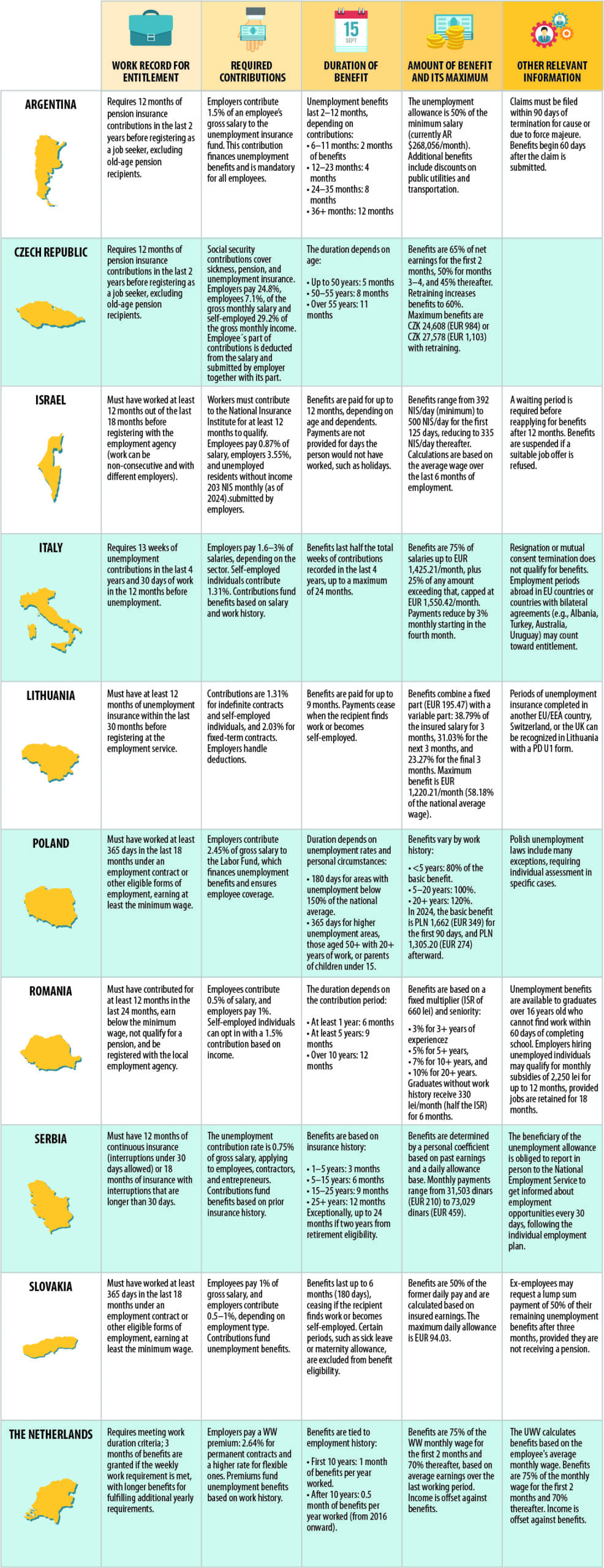
A Quick Guide to Unemployment Insurance Across Borders
FOLLOW US ON LINKEDIN
SEE MORE ALIANT INSIGHTS


